Predator And Prey Food Chain Biology Diagrams Predator-Prey Relationships System. Prof Dr T aleb A. S. Obaid. Modeling efforts of the dynamics of food chains which are initiated long ago confirm that food chains have very rich dynamics. A predator-prey relationship is a fundamental ecological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and consumes another organism, the prey. This dynamic is a cornerstone of ecosystems, shaping populations, behaviors, and evolutionary trajectories. They are also generally lower in the food chain and serve as a vital energy source

Understanding the Food Chain: From Predators to Prey Predator-Prey Relationships. In ecosystems, the food chain is full of predator-prey links. Predators like lions, sharks, and hawks catch their prey to eat, which can be plant-eating animals such as deer or fish. This cycle is key in keeping nature's balance.

What Are the 4 Levels of the Food Chain? Biology Diagrams
A food chain represents the relationship between predator and prey. It is a way of classifying animals, plants, and fungi that eat other organisms in order to survive. The four levels in this food chain are primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and finally decomposers or phytoremediators.

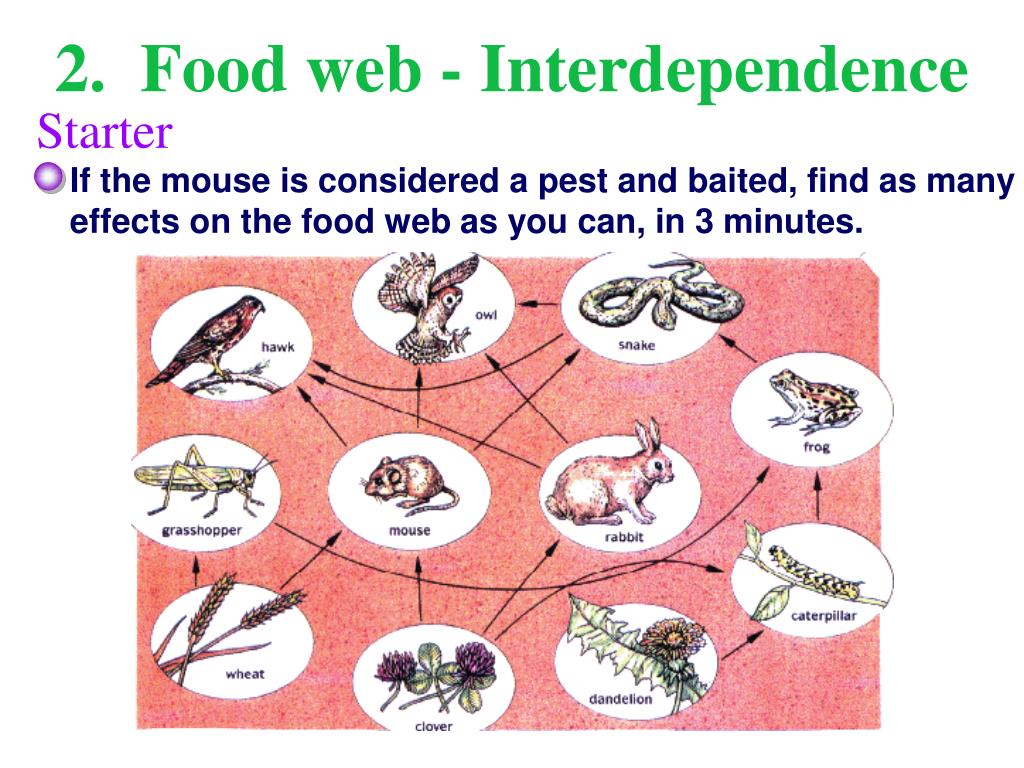
To help you plan your year 7 science lesson on: Predator-prey relationships, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs. Give pupils plenty of opportunities to explore the predators and prey within different food chains. In particular, get pupils to think about those organisms that are only prey, those

National Geographic Society Biology Diagrams
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food chain. A food chain represents a succession of organisms that eat another organism and are, in turn, eaten. Food chains start at the first trophic level with primary producers (plants), followed by herbivores at the second level, predators at the third level, and typically